
Overview
To expand on a basic HTML setup and make it an advanced HTML setup we can add <meta> tags, the lang attribute, and links to external CSS/JS.
In the visualization of an HTML page structure below, the additions that make it advanced are in blue.
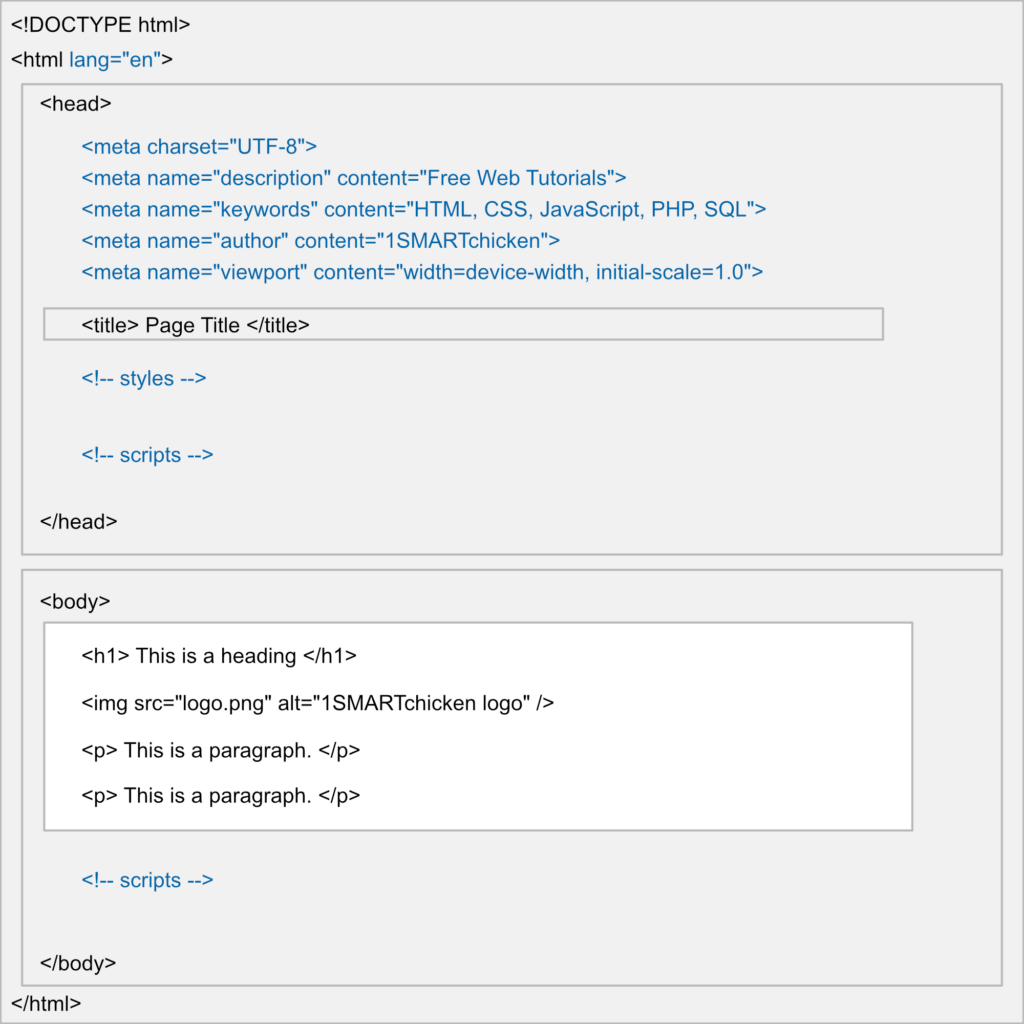
Note
The only thing that will show on the page inside the browser is the area in white (minus the tags of course).
This is the code for the advanced template. I removed the elements inside the <body> to simply things.
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html lang="en-US">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="description" content="Free Web Tutorials">
<meta name="keywords" content="HTML, CSS, JavaScript, PHP, SQL">
<meta name="author" content="1SMARTchicken">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Advanced HTML Template</title>
<!-- styles -->
<!-- scripts -->
</head>
<body>
<!-- scripts -->
</body>
</html>Language Attribute
The first thing we added to the basic template was the lang attribute inside the <html> tag. The lang attribute specifies the language of the element’s content. Common examples are “en” for English, “es” for Spanish, “fr” for French, and so on.
The first example has the language code only. The second includes the country code. The country code isn’t as important, and can be left out if you’re unsure.
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html lang="en"><!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html lang="en-US">Meta Tags
Next we added a series of <meta> tags.
Like the <title>, these tags do not display on the page, but they do tell the browser and search engines information about the document.
There are many <meta> tags with various descriptions for the browser, search engines, and various external services to use. This group below is what are considered the basics that should be included.
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="description" content="Free Web Tutorials">
<meta name="keywords" content="HTML, CSS, JavaScript, PHP, SQL">
<meta name="author" content="1SMARTchicken">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">Note
The <meta> charset should be considered mandatory (it isn’t) as it specifies the character encoding for the HTML document. Similarly, the <meta> name=”viewport” should always be present as it tells the browser to display the page at the width of the device and to scale it to 100% on the initial view. So, not zoomed is what that means.
Finally, we have an area just before the closing </head> tag where we can place styles and scripts.
Styles can be either code chunks of CSS, or better yet, links to external style sheets.
Scripts can similarly be either chunks of JavaScript coded directly on the page, or better yet, links to external .js files.
<title>Advanced HTML Template</title>
<!-- styles -->
<!-- scripts -->
</head>Non-crucial scripts can also be placed just before the closing </body> tag which can speed up the perceived page load time because the page can first render before applying the scripts.
<!-- scripts -->
</body>
</html>Additional information about linking to styles/scripts or placing styles/scripts directly in your document can be found here:
HTML Notes:
- In our HTML section the term “tag” and “element” are often used interchangeably to refer to both the tag used to create a page element and the element created by the tag (<p> tag = <p> element = paragraph on the page)
- HTML5 is not case sensitive; so <P> is the same as <p>, <H1> is the same as <h1>
- Global attributes can be used with all HTML tags and are therefore not mentioned on every tag page
- To write clean, readable HTML code, it is best to use indentation whereas elements within elements are indented (tabbed or spaces) to create something that looks like a project outline
- The browser will automatically remove any extra spaces and lines in your HTML code when the page is displayed
- Double quotes or single quotes can be used around HTML attribute values, but when the attribute value itself contains one form of quote, it will be necessary to use the other around the attribute
We’d like to acknowledge that we learned a great deal of our coding from W3Schools and TutorialsPoint, borrowing heavily from their teaching process and excellent code examples. We highly recommend both sites to deepen your experience, and further your coding journey. We’re just hitting the basics here at 1SMARTchicken.
